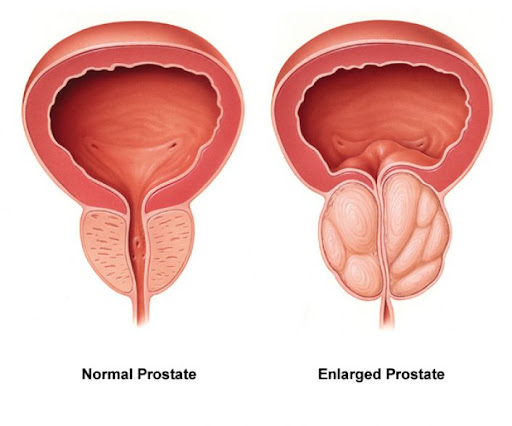
The prostate gland plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system, producing seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. However, as men age, they may experience a common condition known as prostate gland enlargement, also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
Causes of Prostate Gland Enlargement:
The exact cause of prostate gland enlargement is not yet fully understood. However, several factors have been identified as potential contributors to the development of BPH. Hormonal imbalances, specifically an increase in levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone, is believed to play a significant role. Age is also a critical factor, as prostate enlargement becomes more prevalent in men over the age of 50. Genetics, family history, and lifestyle factors such as obesity and lack of physical activity may also contribute to the condition.
Symptoms of Prostate Gland Enlargement:
The symptoms of prostate gland enlargement can vary in severity and impact on an individual’s quality of life. These symptoms can include:
a) Increased urinary frequency: Men with BPH often experience the need to urinate more frequently, particularly during the night (nocturia).
b) Weak urine flow: The flow of urine may become weaker and interrupted, making it difficult to empty the bladder completely.
c) Difficulty starting and stopping urination: Individuals with BPH may experience hesitation or straining when initiating or stopping the flow of urine.
d) Incomplete bladder emptying: The enlargement of the prostate may obstruct the urethra, resulting in the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
e) Urinary urgency: BPH can cause a sudden and urgent need to urinate, making it challenging to hold back urine.
f) Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Obstruction in the urinary tract can increase the risk of UTIs and related complications.
It is essential to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to BPH and can also be associated with other conditions such as prostate cancer. Therefore, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Prostate Gland Enlargement:
To diagnose prostate gland enlargement, a healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and may recommend additional tests. These tests may include:
a) Digital rectal examination (DRE): The healthcare provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to assess the size, shape, and consistency of the prostate gland.
b) Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test: This test measures the levels of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels may indicate prostate enlargement or other prostate-related conditions.
c) Urine flow study: This test evaluates the rate and volume of urine flow, providing insights into potential obstruction caused by an enlarged prostate.
d) Ultrasound: An ultrasound examination may be performed to visualize the prostate gland and assess its size and structure.
Treatment Options for Prostate Gland Enlargement:
The treatment approach for prostate gland enlargement depends on the severity of symptoms, the impact on quality of life, and individual preferences. The available treatment options include:
Treatment options for prostate gland enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), vary depending on the severity of symptoms, the impact on quality of life, and individual preferences. Here are some common treatment approaches:
1. Watchful Waiting/Active Surveillance:
If the symptoms of BPH are mild and not significantly affecting daily life, a healthcare professional may recommend a watchful waiting or active surveillance approach. This involves regular monitoring of symptoms through periodic check-ups to ensure that the condition does not worsen. Lifestyle modifications, such as limiting fluid intake before bedtime and avoiding caffeine and alcohol, may be suggested during this period.
2. Medications:
Several medications are available to manage the symptoms of prostate gland enlargement. These medications work by relaxing the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck, reducing the obstruction and improving urine flow. Commonly prescribed medications include:
a) Alpha-blockers: These medications help relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, relieving urinary symptoms. Examples include tamsulosin, alfuzosin, and doxazosin.
b) 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: These medications reduce the levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to prostate growth. Examples include finasteride and dutasteride. They are particularly effective in reducing the size of the prostate gland over time.
c) Combination therapy: In some cases, a combination of alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors may be prescribed to maximize symptom relief and reduce the risk of disease progression.
3. Minimally Invasive Procedures:
If symptoms persist or worsen despite medication, or if there are complications such as recurrent urinary tract infections or bladder stones, minimally invasive procedures may be considered. These procedures aim to remove or reduce excess prostate tissue, thus relieving the obstruction. Some common minimally invasive procedures include:
a) Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): This is a surgical procedure in which the surgeon removes the excess prostate tissue using a resectoscope inserted through the urethra. TURP is considered the gold standard treatment for BPH and provides significant symptom relief.
b) Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP): In this procedure, small incisions are made in the prostate to widen the urethra and improve urine flow. It is typically recommended for men with smaller prostate glands.
c) Laser therapy: Various laser techniques, such as laser vaporization, laser enucleation, and photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP), are used to remove or ablate excess prostate tissue. These procedures offer a minimally invasive alternative to TURP, with shorter recovery times and fewer complications.
d. Surgical Interventions:
In cases of severe BPH or when other treatments have not been effective, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include:
i) Open prostatectomy: This traditional surgical procedure involves removing the entire prostate gland through an abdominal incision. It is typically reserved for very large prostates or when other treatments are not feasible.
ii) Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT): This procedure uses heat generated by microwave energy to destroy excess prostate tissue. It is typically performed on an outpatient basis and may require multiple sessions.
Written by profT for naijatipsland.com










