Gravity is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, along with electromagnetism, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force. It is the weakest of these forces, but it is also the most pervasive. On Earth, gravity is the force that pulls us down to the ground, keeping us from floating off into space. It also causes objects to fall towards the ground when they are dropped.
The force of gravity is proportional to the mass of the two objects involved and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This means that the more massive an object is, the greater its gravitational pull will be. It also means that the farther apart two objects are, the weaker the gravitational force between them will be.
The gravitational force between two objects is always attractive, meaning that it always pulls them towards each other. This is why objects fall down to the ground and why planets orbit the sun.
The strength of the gravitational force between two objects is determined by their masses and their distance from each other. The more massive an object is, the greater its gravitational pull will be. The farther apart two objects are, the weaker the gravitational force between them will be.
The gravitational force between two objects is also affected by the presence of other objects. For example, the gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth causes the tides. The gravitational pull of the sun on the Earth keeps the Earth in orbit around the sun.
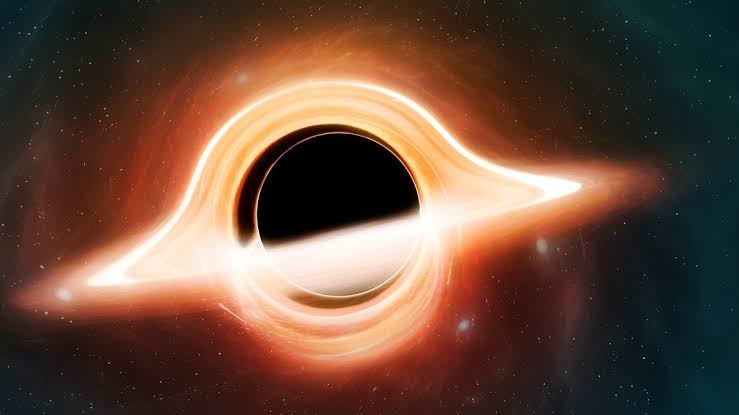
Black holes are regions of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. They are formed when a star with a mass greater than about three solar masses collapses under its own gravity. The gravitational force of a black hole is so strong that it can pull in anything that comes too close, even light.
The boundary of a black hole is called the event horizon. Once an object crosses the event horizon, it is impossible for it to escape. The event horizon is a point of no return.
Black holes are invisible because they do not emit any light. However, they can be detected by their gravitational effects on nearby objects. For example, astronomers can observe the effects of black holes on the motion of stars and gas in the surrounding area.
Black holes are one of the most mysterious objects in the universe. Scientists are still learning about their properties and how they work.
Written by profT for Naijatipsland.com










