Oluwatobiloba Jaiyeola
A dental care expert, Dr. Agho Theophilus has cautioned Nigerians against brushing right after engaging in oral sex, noting that it is bad for oral health.
Theophilus who is a consultant of oral medicine at the Ahmadu Bello University Teaching Hospital Zaria, Kaduna State, said brushing immediately after engaging in oral sex could also lead to the transmission of STIs.
Theophilus explained further that when an individual has injuries in their mouth if they brush immediately after engaging in oral sex, there is a tendency that bacteria could pass through these sores.
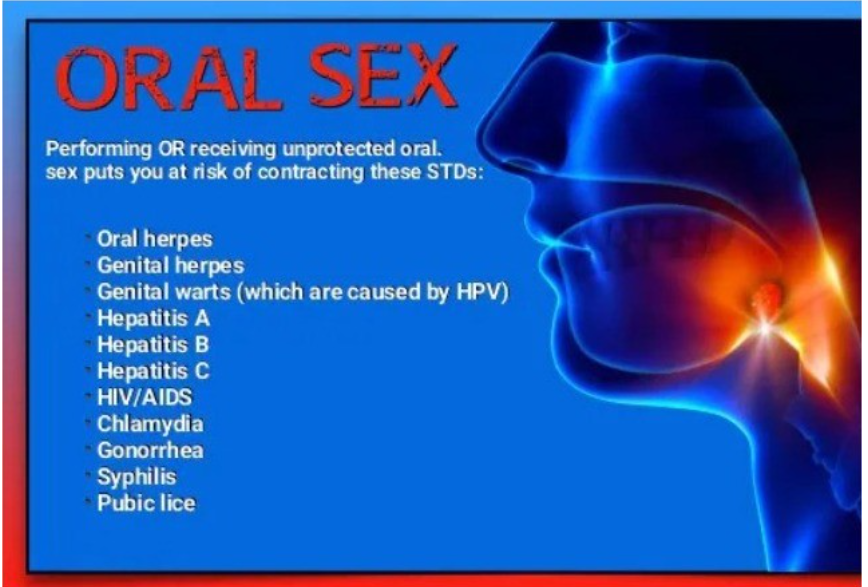
Speaking in an interview with PUNCH HealthWise, Dr. Theophilus said, “It is not appropriate to brush immediately after oral sex because patients are exposed to dental health risks like gonorrhoea, syphilis, chlamydia, HIV, herpes, human papillomavirus virus also known as genital wart and hepatitis A, B, and E.
“This is because when people brush their oral cavity, sometimes they may have injuries or cuts and these injuries may serve as a point in which bacteria may pass through and from there it can enter inside the bloodstream, so it is advised that they delay it. The advisable thing is to delay it for at least 30 minutes,” he said.
On how to maintain proper oral hygiene after sex, the dental care expert said, “The patient should wait for at least 30 minutes after engaging in oral sex before brushing. The individual can also engage in flossing the teeth before having oral sex.
“Some studies have said that the use of alcohol mouth rinse/wash could kill some of those bacteria.
“Another thing is, rinsing out your mouth with water can also be helpful, not brushing immediately, wait 30 minutes after the action.”
Theophilus urged Nigerians to engage in the use of physical barriers to prevent oral infections gotten from oral sex.
“Use of physical barriers like condoms, use of what we call dental or oral damns, there is also plastic wrap for people that do oral sex on the anus. Those are some of the physical barriers that can be used in preventing oral infection,” he said.
Dental dams he said, are like a protective shield which is usually a thin, flexible piece of latex or polyurethane sheets. These sheets protect against direct mouth-to-genital or mouth-to-anus contact during oral sex, and also reduce the risk for STIs while still giving room for stimulation.
Theophilus further stressed that a patient who has just recently undergone a dental procedure or treatment should not engage in oral sex because of the risks involved.
He said, “People need to avoid oral sex if their partner has known STIs. Also, if there are any open wounds or sores in the genitals of their partners, they should equally avoid oral sex.
“Oral sex should also be avoided with women during their menstrual periods.
“Persons engaging in oral sex should also ensure their genitals, as well as the surrounding area, is washed and cleaned thoroughly.
“People should limit the number of sexual partners they have and avoid casual sex, it is also important that people should have regular health checks and screening. Note that self-education is also important.”
The dental health expert also urged the government to promote HPV vaccination in men, noting that this will help in reducing HPV infection that results from sex, for men who practice the various types of oral sex like fellatio, cunnilingus, and anilingus.
“Fellatio is the oral stimulation of a man’s genital area, cunnilingus is the act of orally stimulating the female genitals and anilingus is the licking of the anus by the tongue or mouth.”
According to the National Institutes of Health, “Oral sex is commonly practiced by sexually active male-female and same-gender couples of various ages, including adolescents.
“Oral health has a direct impact on the transmission of infection; a cut in your mouth, bleeding gums, lip sores or broken skin increases the chances of infection.
“Although oral sex is considered a low-risk activity, it is important to use protection and safer sex precautions. There are various methods of preventing infection during oral sex such as physical barriers, health, and medical issues, ethical issues, and oral hygiene and dental issues.
“The injury or unhealthy periodontal status of oral cavity accelerates the occurrence of transmission of infections into the circulation. Thus consequences of the unhealthy or painful oral cavity are significant and oral health should be given paramount importance for the practice of oral sex,” the NIH said.










